JupyterLab
JupyterLab is a next-generation, web-based interactive development environment that supports Python, data visualization, and AI application development. It is especially well-suited for use on the Jetson platform. This guide provides step-by-step instructions on how to install, launch, and configure JupyterLab on Jetson.
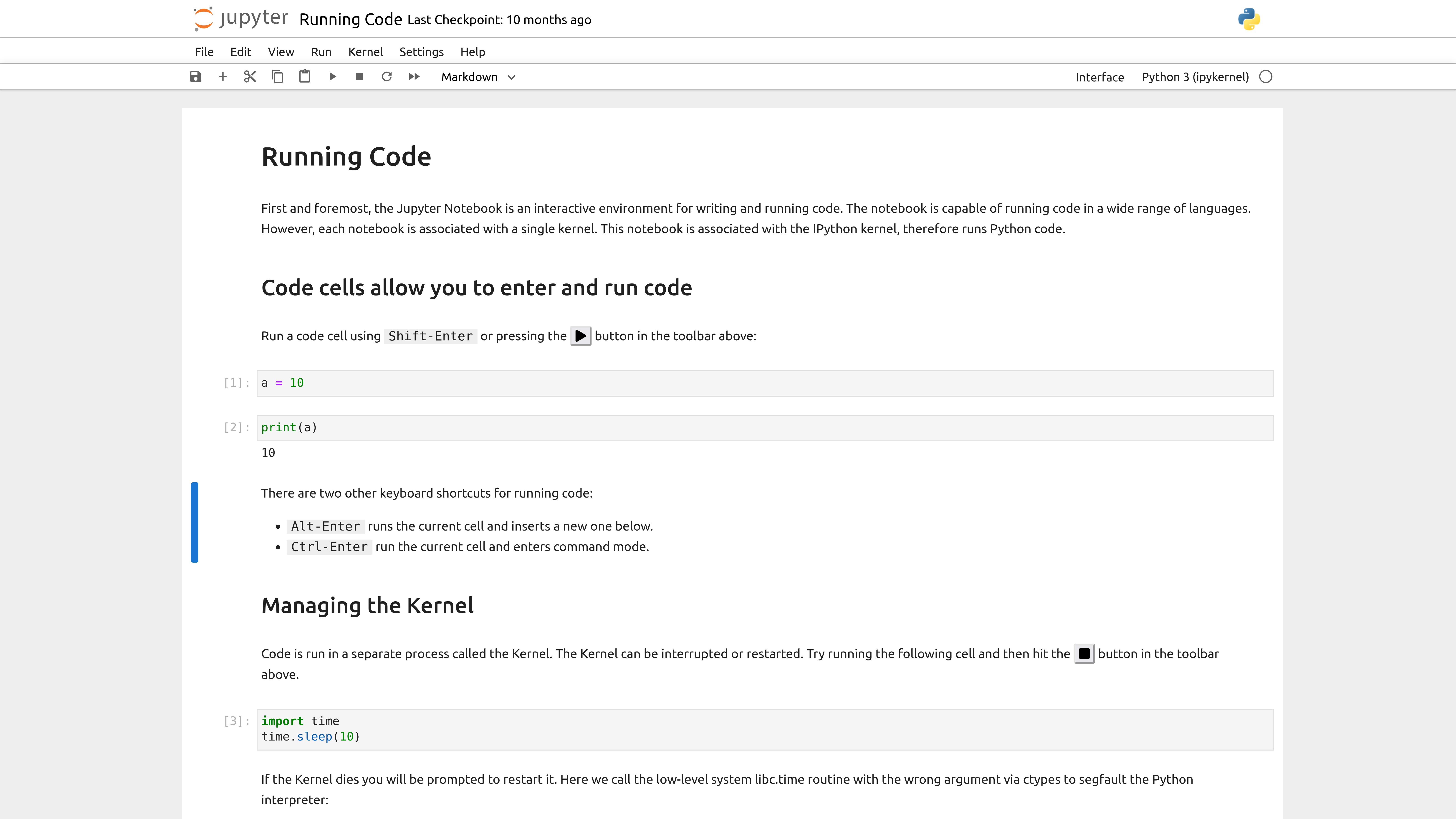
1. Overview
JupyterLab offers an interactive development environment with the following features:
- Execute Python, C++, and CUDA code interactively
- Support for Markdown and data visualizations
- Multi-tab interface with integrated terminal, text editor, and graphical tools
- Compatible with ARM64 architecture — ideal for Jetson platforms
- Remote access via web browser
This guide covers:
- Installation via
pip - Configuration and remote access setup
- Enabling autostart as a service
- Uninstallation and troubleshooting
2. Requirements
Hardware
| Component | Minimum Requirement |
|---|---|
| Device | Jetson Orin Nano / NX |
| Memory | ≥ 4GB (8GB recommended) |
| Storage | ≥ 1GB available space |
Software
- JetPack 5.x (based on Ubuntu 20.04 or 22.04)
- Python 3.8 or higher
pipandvenvtools- (Optional) Conda / virtualenv for environment management
3.Installation
Method A: Install via pip (Recommended)
sudo apt update
# Upgrade pip and install jupyterlab
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install jupyterlab
# Verify installation
jupyter-lab --version # Should return a version number
✅ The pip method is the most flexible and fully compatible with Jetson systems.
4. Launching and Accessing JupyterLab
Start JupyterLab
jupyter-lab --ip=0.0.0.0 --port=8888 --no-browser
This will output an access URL with a token in the terminal.
Access via Browser
Launch a web browser and navigate to the following address:
http://<Jetson-IP>:8888/lab
5. Create Configuration File (Optional)
To customize and persist JupyterLab settings, generate a configuration file:
jupyter lab --generate-config
Edit the file using a text editor:
nano ~/.jupyter/jupyter_lab_config.py
Recommended configuration options:
c.ServerApp.ip = '0.0.0.0' # Allow remote access
c.ServerApp.port = 8888 # Set port number
c.ServerApp.open_browser = False # Do not auto-launch browser
c.ServerApp.root_dir = '/home/your_username/notebooks' # Default working directory
6.Set Up Auto-Start Service (Optional)
To enable JupyterLab to launch automatically at system startup, create a systemd service file:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/jupyter.service
Insert the following configuration (replace your_username with your actual username):
[Unit]
Description=JupyterLab
[Service]
Type=simple
User=your_username
ExecStart=/home/your_username/.local/bin/jupyter-lab --config=/home/your_username/.jupyter/jupyter_lab_config.py
WorkingDirectory=/home/your_username
Restart=always
RestartSec=10
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Start the service:
sudo systemctl daemon-reexec
sudo systemctl enable jupyter
sudo systemctl start jupyter
7. Common Commands
| Action | Command |
|---|---|
| Start the service | sudo systemctl start jupyter |
| Stop the service | sudo systemctl stop jupyter |
| Check service status | systemctl status jupyter |
| View real-time logs | journalctl -u jupyter -f |
8. Troubleshooting
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Unable to access the web page | Ensure port 8888 is open on the Jetson device |
| Lost or unknown token | Run jupyter lab list to view active instances and tokens |
| Unable to save files | Check if the notebooks directory has proper write permissions |
| Web interface not loading properly | Clear browser cache or restart the Jupyter service |
9. Appendix
Default Paths
| Purpose | Path |
|---|---|
| Default notebooks directory | /home/jetson/notebooks |
| Configuration file | ~/.jupyter/jupyter_lab_config.py |
| Web UI address | http://<Jetson-IP>:8888/lab |